Networkx is a python package for working with graphs and networks. Networkx is capable of creating a graph from within a python script, but you may also want to load a graphs from file. This post looks at some of the ways networkx allows you to load graphs from file, and gives some simple examples to help you get started.
If you have automatically produced a graph, such as from analysis of social media, then you may have a graph file format in mind. If you are making a graph from scratch you may prefer to write it into a separate file rather than having it saved along side your networkx python code.
Simple Load Graphs From File
Networkx node lists are just lists of python objects. Edge lists are lists of tuples representing the connections between nodes. If your graph nodes are just names then you can use simple methods to read them from a file.
First let’s create a node file which we will think of as a list of node labels (I called it ‘nodes.txt’).
node_1 node_2 node_3 node_x
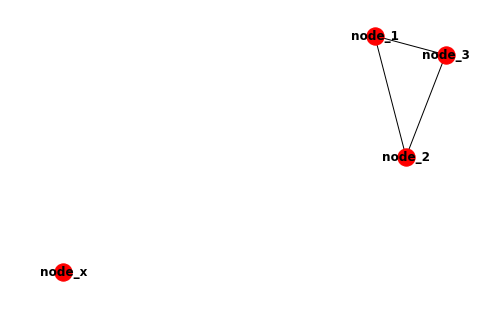
I am including an extra node in here that does not feature in the file containing edges. This is to show how you can include unconnected nodes. If all of your nodes are connected, you can actually just use a list of edges as networkx will add all the nodes it needs.
Since networkx will create any nodes in the edges file, you can use the node list to only include isolated nodes, like this:
node_x
And here’s the corresponding edge file – ‘edges.txt’. Notice how ‘node_x’ does not feature in this list.
node_1 node_2 node_2 node_3 node_3 node_1
We can now load these two files into network x:
import networkx as nx
my_graph = nx.Graph()
edges = nx.read_edgelist('edges.txt')
nodes = nx.read_adjlist("nodes.txt")
my_graph.add_edges_from(edges.edges())
my_graph.add_nodes_from(nodes)
nx.draw(my_graph, with_labels=True, font_weight='bold')
This should draw a graph similar to this:
Use Graph Modelling Language
You may also want to load your graph saved in GML format – a way of representing a graph in a plain text file. Networkx can read and write gml files which contain both node and edge information. This might be a more attractive option if you also want to record additional attributes about the nodes and edges.
Here is a simple example gml file which I have saved as ‘gml_graph.gml’ (slightly modified from here):
graph [ comment "This is a sample graph" directed 0 label "Hello, I am a graph" node [ id 1 label "node 1" ] node [ id 2 label "node 2" ] node [ id 3 label "node 3" ] node [ id 4 label "node x" ] edge [ source 1 target 2 label "Edge from node 1 to node 2" ] edge [ source 2 target 3 label "Edge from node 2 to node 3" ] edge [ source 3 target 1 label "Edge from node 3 to node 1" ] ]
We can easily load this into networkx with
import networkx as nx
my_graph = nx.Graph()
gml_graph = nx.read_gml('./gml_graph.gml')
nx.draw(gml_graph, with_labels=True, font_weight='bold')
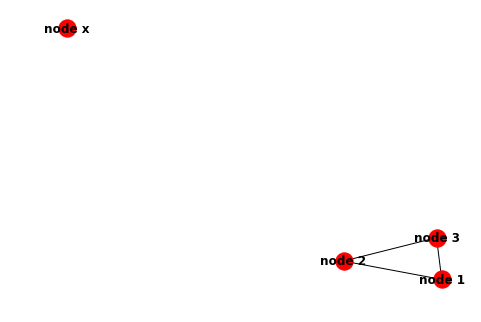
Which should draw a graph like the one below. This is essentially the same as the graph in the previous example: nodes 1, 2 and 3 are connected together, while node x is on its own.
Other Methods
Networkx has a range of other methods to load graphs from file which you may want to consider. Networkx is also quite flexible in which python object types can be used as nodes, so you may be able to work beyond the methods included with the package, such as with dictionaries.